Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumoto, Taro; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Li, J.*
Denki Gakkai Purazuma Kenkyukai Shiryo (PST-05-17), p.83 - 86, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Shimyureshon, 22(2), p.89 - 97, 2003/06
This is a collection of review article related to the "Multiple Time and Spatial Scale Plasma Simulation" of various fields including fundamental research area of self-organization, magnetic and laser fusion field, space and astrophysics field where a plasma plays an essential roles.
Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Kim, J.*; Horton, W.*; Tajima, Toshiki*; LeBrun, M. J.*; Dettrick, S. A.*; Li, J.; Shirai, Hiroshi
Nuclear Fusion, 40(3Y), p.667 - 676, 2000/03
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:78.61(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Progress of confinement studies on ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using the gyrokinetic full-f Eulerian code GT5D is reviewed. GT5D enabled long time turbulence calculations with fixed heating power, where turbulent transport and plasma profiles are determined in a consistent manner. In heating power scan of the ITG turbulence, the power degradation of confinement, which is universally observed in tokamak experiments, is recovered. The plasma size scaling of the confinement is studied using ITER-size numerical experiments, and it is found that confinement properties of large devices are affected by the heating power scaling. Relations between the plasma size scaling and differences of confinement properties between hydrogen and deuterium plasmas are clarified.
Nakata, Motoki; Honda, Mitsuru; Yoshida, Maiko; Urano, Hajime; Maeyama, Shinya; Nunami, Masanori*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*
no journal, ,
First-principle based gyrokinetic simulation is a powerful method for investigating turbulent transport in magnetically confined fusion plasmas, and the quantitative evaluations of the prediction capability through comparisons with existing experiments and the model improvement are important issues. In this study, a local gyrokinetic turbulence code GKV-J is extended to incorporate realistic tokamak equilibria to realize the first principle based turbulent transport simulations on JT-60U tokamak. In addition to clarifications of the micro-stability properties depending on the radial locations, the turbulence simulation results successfully reproduce the experimental results on ion and electron heat diffusivity in the core region, where the conventional fluid-type reduced transport model shows some deviations. Also, the impact of shaping on turbulent transport properties is identified for JT-60SA tokamak.
Nakata, Motoki; Honda, Mitsuru; Yoshida, Maiko; Urano, Hajime; Maeyama, Shinya; Nunami, Masanori*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*
no journal, ,
First-principle based gyrokinetic simulation is a promising approach for investigating turbulent transport in future burning plasmas such as ITER an DEMO. In this study, ITG-TEM driven turbulent transport simulations on the realistic JT-60U tokamak equilibrium are realized by using a local gyrokinetic turbulence code GKV-J. Linear micro-stability analyses on several radial locations revealed that ITG, ITG-TEM, and TEM modes are dominant for inner, middle, and outer core regions, respectively. The nonlinear turbulence simulation results successfully reproduce the experimental results on ion and electron heat diffusivity in the core region, where the conventional fluid-type reduced transport model shows some deviations. Also, different nonlinear dependences of the turbulence/zonal-flow energy on the ion/electron heat and particle transport levels are newly identified, i.e., weaker impact on the electron heat and particle transport compared to the ion heat one.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Differences of confinement properties between hydrogen and deuterium plasmas are studied in numerical experiments of ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using a full-f gyrokinetic code. Through systematic heating power and plasma size scans, it is found that a Bohm like scaling of the confinement time 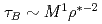 is given by stiff ion temperatur profiles, which are produced by intermittent bursts of avalanche like non-local transprt. Here,
is given by stiff ion temperatur profiles, which are produced by intermittent bursts of avalanche like non-local transprt. Here,  is the mass of ions and
is the mass of ions and 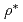 is the normalized Larmor radius. From this result, it is shown that the confinement time of the ion temperature gradient turbulence is proportional to the mass of ions.
is the normalized Larmor radius. From this result, it is shown that the confinement time of the ion temperature gradient turbulence is proportional to the mass of ions.
Yagi, Masatoshi; Seto, Haruki; Cho, Y. W.*; Hahm, T. S*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Decaying turbulence simulations of ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence with adiabatic electrons and ion temperature gradient driven trapped electron mode (ITG-TEM) turbulence with kinetic electrons are performed using a full-f gyrokinetic code. Nonlinear critical temperature gradients exceeding linear critical temperature gradients are observed in both simulations, and mechanisms to sustain them are investigated. It is found that unlike zonal flows in the ITG turbulence, the ITG-TEM turbulence produces corrugated electron density profiles, which form radial electric fields with strong shear following a force balance relation.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Obrejan, K.; Asahi, Yuichi*; Matsuoka, Seikichi*
no journal, ,
To enable low cost experimental data analyses Transient plasma responses due to modulated electron heating are investigated in numerical experiments of ion temperature gradient driven trapped electron mode turbulence using gyrokinetic full-f Eulerian code GT5D. It is found that even with electron heating without particle and momentum sources such as electron cyclotron resonance heating, dominant turbulence is changed from ion turbulence to electron turbulence due to changes of the electron temperature gradient and the temperature ratio, and the resulting turbulent transport produces responses of density and rotation profiles.